

Monosaccharide includes a cyclic-hemiacetal structure in which there is an oxide ring between carboxyl carbon and C₄, C₅, or C₆ carbon atoms.It is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of saccharide and the hydroxyl group of some compounds such as alcohol.Therefore, they are important for the formation of oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. And when a long chain of sugar molecules is linked it is called a polysaccharide.Several sugar molecules are linked together and are known as oligosaccharides.When two sugar molecules are joined by a glycosidic bond it forms a disaccharide.The type of covalent bond formed between the aldehyde or ketone group of one sugar molecule and the hydroxyl group of another sugar molecule is called a glycosidic bond.

For example, Sucrose, cellulose, and maltose are formed by the joining of two or more monosaccharide units.
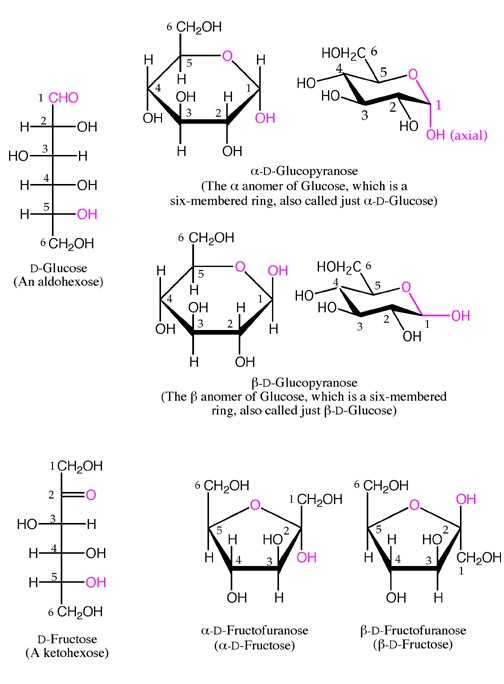
Know in one minute about glycosidic bond.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
